Response to Intervention (RTI) efforts aim to identify students’ learning and behavioral problems early so that educators can intervene with individualized instruction. When implemented well, RTI improves instruction and increases students’ chance of school success.
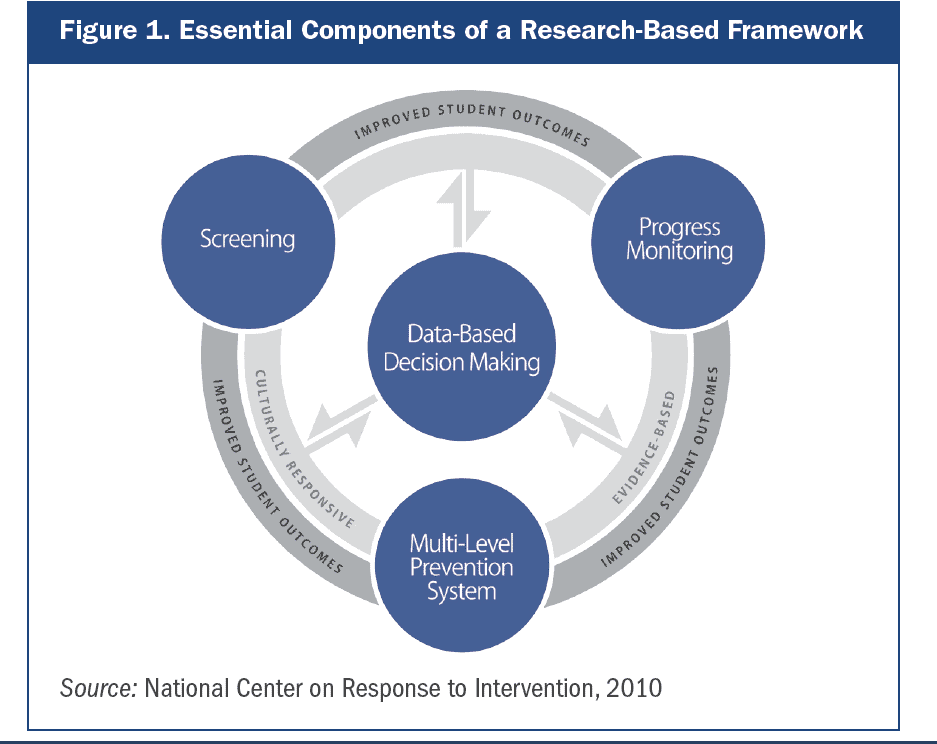
But what does an effective RTI program look like? The National Center on RTI says the four essential components of a research-based framework for RTI are: universal screening, continuing progress monitoring, multi-level prevention system, and data-based decision making.
1. Universal screening
Universal screening is the first component for RTI. This assessment is used to help identify which students are under-resourced for poor learning outcomes. These screenings usually include a brief assessment with all students in a specific grade level followed by additional testing or progress monitoring to determine which students are under-resourced. The screening takes into consideration student strengths, cultural responsiveness, and linguistics.
2. Progress monitoring
The RTI framework includes progress monitoring to track students’ academic performance and rate of learning. This component also evaluates the success of classroom instruction for improving individual or classroom student learning. Progress monitoring also takes into consideration student strengths, cultural responsiveness, and linguistics.
3. Multi-level prevention system
The multi-level prevention system has three levels: primary, secondary and intensive. This key piece is used school wide and each level represents a specific amount of intervention based on a student’s responsiveness to learning materials.
The primary prevention level is focused on high quality core instruction. The secondary level identifies students who are at risk for poor learning outcomes and delivers targeted, supplemental instruction to small groups. Intensive intervention includes individualized intervention for students who have little response to the primary or secondary prevention levels.
4. Data-based decision making
All levels of RTI and all levels of instruction include data analysis and decision making. Decisions concerning instruction, movement within the various levels, and identifying learning disabilities are applied by educators who use the screening and progress monitoring data.
Waterford curriculum can be used at all three levels of the prevention system as a intervention tool. When students start Waterford, the curriculum assesses their level and places them accordingly; then, it delivers differentiated instruction at each child’s ability level and pace, monitoring their progress as they go. Reports and dashboards inform instruction and help teachers quickly and easily identify struggling students and pain points.
Want to know more about RTI? Several materials are available to visualize and learn more about the RTI framework, including an RTI chart and other resources, on RTI4Success.org.